E-Commerce
Work Programme on E-Commerce
The Work Programme on Electronic Commerce, adopted by the General Council in September 1998, tasks four WTO bodies with exploring the relationship between existing WTO agreements and e-commerce. It gives the General Council a central role of continuous review of the Programme, with responsibility for exploring cross-cutting issues and examining a provisional moratorium on customs duties on electronic transmissions. The overall objective is to examine all trade-related aspects of e-commerce and to give recommendations for further action.
Work Programme Meetings
News
Origin of the Programme
In response to the growing importance of e-commerce, ministers adopted the Declaration on Global Electronic Commerce at the Second Ministerial Conference in May 1998. The Declaration called for:
- the establishment of a work programme
- a provisional moratorium on customs duties on electronic transmissions
In September 1998, the General Council adopted the Work Programme on Electronic Commerce to examine trade-related issues relating to global e-commerce.
Documents
What is e-commerce?
The Work Programme on Electronic Commerce states: “Exclusively for the purposes of the work programme, and without prejudice to its outcome, the term 'electronic commerce' is understood to mean the production, distribution, marketing, sale or delivery of goods and services by electronic means”.
Where is the Work Programme conducted?
The Work Programme instructed four WTO bodies to explore the relationship between existing WTO agreements and e-commerce:
- the Council for Trade in Services examines and reports on the treatment of e-commerce in the legal framework of the General Agreement on Trade in Services;
- the Council for Trade in Goods examines and reports on aspects of e-commerce relevant to the provisions of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) 1994, the multilateral trade agreements covered under Annex 1A of the WTO Agreement and the approved work programme;
- the Council for Trade-related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) examines and reports on the intellectual property issues arising in connection with e-commerce;
- the Committee on Trade and Development examines and reports on the development implications of e-commerce, taking into account the economic, financial and development needs of developing countries.
Relevant reports and other useful information and documentation on the Work Programme can be found in the eLibrary on E-Commerce.
What is the role of the General Council?
The General Council keeps the Work Programme under continuous review. In addition, it explores trade-related issues of a cross-cutting nature and examines all aspects of the Work Programme concerning the imposition of customs duties on electronic transmission.
Between 2001 and 2016, the General Council's examination of cross-cutting issues was carried out in dedicated discussions. After 2016, discussions have continued in informal meetings open to all members convened by the General Council Chair and through reviews in the General Council. More information on these discussions is available here.
In 2015, the Secretariat circulated a background note providing a summary of the activities of the bodies charged with implementing the Work Programme. This was updated in 2016.
Work under the Work Programme on e-commerce has intensified following the MC12 Decision which called for the reinvigoration of the Work Programme with particular emphasis on its development dimension. The Decision also requested Members to intensify discussions on the scope, definition, and impact of the moratorium. Work has resumed in Dedicated Discussions addressing specific issues identified by Members, including issues related to the moratorium.
More information on recent discussions is available here.
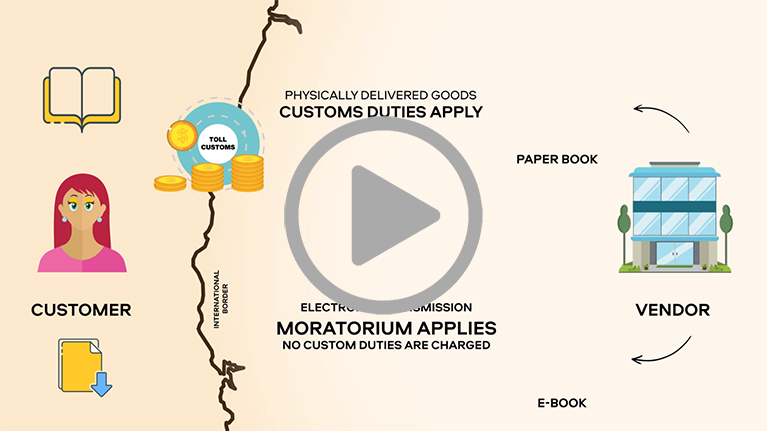
Customs duties
Products that were always traded physically are now increasingly traded digitally, with e-books and streaming services progressively taking the place of printed books, CDs or DVDs. Customs duties are usually applied by WTO members on imported goods and services but since 1998 they have agreed not to impose tariffs on electronic transmissions.
Ministerial Conferences
Ministers have considered the Work Programme on Electronic Commerce at nearly all Ministerial Conferences. Ministers have taken note of the work undertaken and instructed the General Council and subsidiary bodies to continue this work. Ministers have also agreed to continue the practice of not imposing customs duties on electronic transmissions until their next ministerial conference. For more information on declarations and decisions, please click here.






